Short Version
The fair value gap refers to the discrepancy or difference between the market price of an asset or investment and its estimated fair value. Fair value represents the objective worth of an asset based on factors such as supply and demand, financial performance, and market conditions. When the market price deviates from this estimated value, a fair value gap emerges. Understanding and closing this gap is crucial for accurate pricing, informed investment decisions, and maximizing returns. Factors such as market trends, behavioral biases, information asymmetry, and external influences can contribute to the fair value gap. Strategies like robust valuation methodologies, data-driven decision making, risk assessment, and transparency can help bridge this gap and achieve fairer pricing.
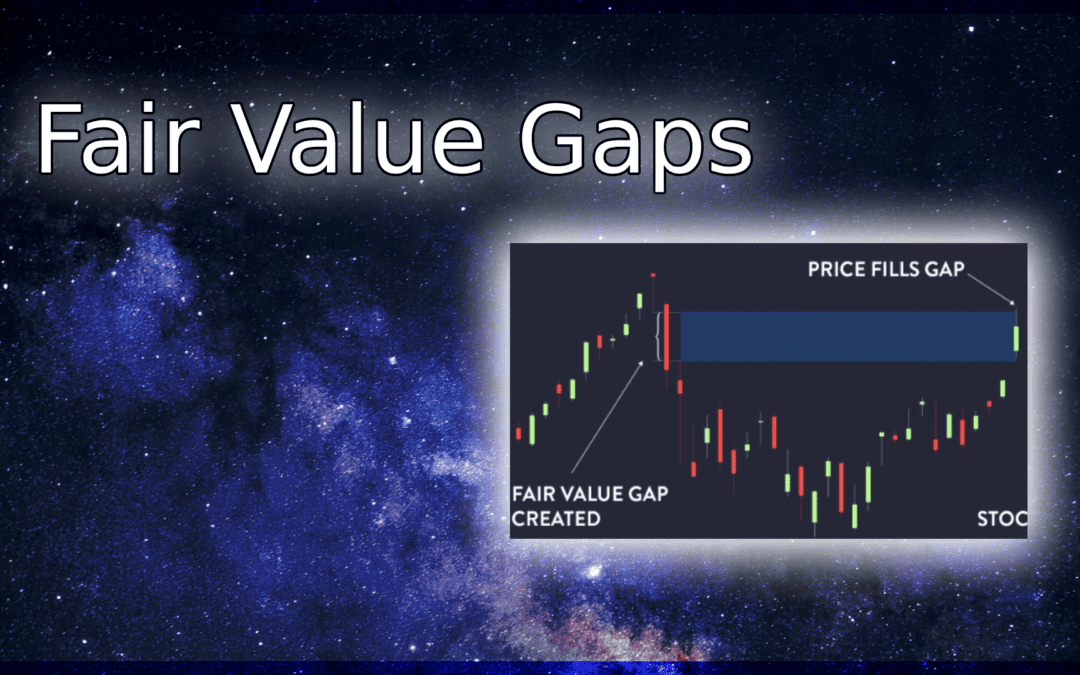
Examples of Fair Value Gaps
You can find more examples of Fair Value Gaps in the community Discord under the 🧠|trading-library forum
Videos
Additional Resources
Long Version
Introduction
The Fair Value Gap: Unveiling the Key Factors for Accurate Pricing
When it comes to pricing assets and investments, accurately determining their fair value is crucial. However, a common challenge faced by investors and businesses alike is the existence of the fair value gap. In this blog post, we will delve into the concept of fair value gaps, their significance in pricing, and the key factors that contribute to them. Join us as we explore the strategies and insights necessary to bridge this gap and achieve accurate pricing for maximum value.
Discover how understanding fair value gaps can revolutionize your investment decisions and help you navigate the complex world of asset valuation. Stay tuned as we uncover the reasons behind fair value gaps and shed light on the essential factors influencing pricing accuracy. By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and tools needed to close the fair value gap and make informed investment choices.
Let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries of fair value gaps together!
Understanding Fair Value Gaps
What Are Fair Value Gaps?
Fair value gaps refer to the discrepancies that occur when the market price of an asset or investment deviates from its fair value. Fair value represents the estimated worth of an asset based on objective factors such as supply and demand, financial performance, and market conditions. When the market price fails to align with this estimated value, a fair value gap emerges.
Examples of Fair Value Gaps
Fair value gaps can manifest in various scenarios. For instance, consider a situation where a company’s stock price is significantly higher or lower than its intrinsic value. This disparity creates an opportunity for savvy investors to capitalize on the mispricing.
Another example is the real estate market, where the perceived value of a property may not align with its fair value due to factors such as location, market trends, or emotional attachments. Understanding fair value gaps in real estate can help buyers and sellers make more informed decisions.
The Significance of Closing Fair Value Gaps
Closing fair value gaps is essential for several reasons. First and foremost, accurate pricing ensures that investors pay a fair price for their investments, reducing the risk of overpaying or underselling. Furthermore, accurate valuation contributes to market efficiency and stability.
Additionally, closing fair value gaps promotes investor confidence and trust in the market. When prices align closely with fair values, market participants are more likely to engage in transactions and make sound investment decisions.
Stay tuned as we explore the key factors that contribute to fair value gaps and uncover strategies to bridge these gaps effectively. By understanding the intricacies of fair value gaps, you can position yourself for success in the world of asset valuation and pricing.
Factors Contributing to Fair Value Gaps
Market Trends and Volatility
Market dynamics play a significant role in creating fair value gaps. Fluctuations in supply and demand, economic conditions, and investor sentiment can all contribute to pricing discrepancies. Understanding market trends and volatility is crucial in accurately assessing fair value and navigating the ever-changing landscape of investments.
Behavioral Biases
Human behavior can introduce biases that distort fair value. Emotional decision-making, herd mentality, and cognitive biases such as anchoring or overconfidence can lead to irrational pricing. Being aware of these biases and implementing strategies to mitigate their impact is essential for closing fair value gaps.
Information Asymmetry
Uneven access to information among market participants can create unfair advantages and contribute to fair value gaps. Some individuals or entities may possess privileged information, while others lack crucial insights. Addressing information asymmetry through transparency, disclosure, and improved data dissemination can help level the playing field and enhance pricing accuracy.
External Influences
External factors beyond an asset’s intrinsic value can also affect fair value. Regulatory changes, geopolitical events, technological advancements, and competitive pressures can impact pricing. Analyzing and understanding these external influences is vital in accurately assessing fair value and predicting market movements.
Stay tuned as we delve deeper into these factors and explore strategies for closing the fair value gap. By identifying and addressing these key contributors, you can enhance your ability to make informed investment decisions and achieve accurate pricing.
Strategies for Closing the Fair Value Gap
Robust Valuation Methodologies
Implementing robust valuation methodologies is crucial for closing fair value gaps. Utilize a combination of quantitative models, financial ratios, discounted cash flow analysis, and market comparisons to derive accurate valuations. By employing rigorous and comprehensive valuation techniques, you can minimize pricing discrepancies and achieve fairer assessments.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Data is a powerful tool in bridging the fair value gap. Utilize reliable and up-to-date data to inform your valuation and pricing decisions. Leverage market research, industry trends, financial statements, and comparable transaction data to gain insights into fair value. The more informed your decisions are, the better equipped you will be to close the gap between market prices and intrinsic value.
Risk Assessment
Assessing and managing risks is crucial for accurate pricing. Identify potential risks and uncertainties that could impact an asset’s fair value, such as market volatility, regulatory changes, or competitive threats. Conduct comprehensive risk analyses to factor in these variables and adjust valuations accordingly. By considering risk factors, you can make more informed pricing decisions and narrow the fair value gap.
Transparency and Disclosure
Transparency and disclosure are essential in closing fair value gaps. Communicate openly with stakeholders, providing clear and accurate information regarding an asset’s value drivers, risks, and potential market impacts. Promote transparency through comprehensive financial reporting, disclosure of assumptions and methodologies, and sharing relevant market data. Transparency builds trust and reduces information asymmetry, leading to fairer pricing outcomes.
Stay tuned as we explore real-life case studies and success stories where these strategies have been successfully implemented. By adopting these approaches, you can enhance your ability to bridge the fair value gap and achieve more accurate pricing for your investments.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Case Study 1: Company X – Closing the Fair Value Gap in the Tech Industry
In the highly competitive tech industry, Company X successfully closed the fair value gap by implementing a comprehensive valuation framework. By utilizing advanced quantitative models and conducting thorough market research, they accurately assessed the fair value of their products and services. This enabled them to price their offerings competitively and attract more customers, leading to increased market share and profitability.
Case Study 2: Investor Y – Leveraging Data-Driven Decision Making
Investor Y, an astute market participant, closed the fair value gap by leveraging data-driven decision making. They extensively analyzed market trends, financial statements, and comparable transactions to identify undervalued assets. By making informed investment decisions based on reliable data, Investor Y was able to acquire assets at favorable prices. Over time, as market prices aligned with their fair values, Investor Y realized significant returns on their investments.
Success Story 1: Bridging the Gap in Real Estate
In the competitive real estate market, Developer Z successfully bridged the fair value gap by implementing transparency and disclosure practices. They provided detailed property valuations, comprehensive market analyses, and full disclosure of any potential risks or limitations. This approach enhanced investor confidence and trust, resulting in faster sales and higher selling prices. By emphasizing transparency, Developer Z achieved fairer pricing outcomes and built a reputation for integrity in the industry.
Success Story 2: Risk Management and Accurate Valuation
Investment Firm A effectively closed the fair value gap by integrating robust risk management practices into their valuation process. They conducted thorough risk assessments, identifying potential factors that could impact fair value. By incorporating risk factors into their valuations, Investment Firm A achieved more accurate pricing, reduced pricing discrepancies, and enhanced their overall investment performance.
Stay inspired by these case studies and success stories, showcasing how businesses and individuals have successfully closed fair value gaps. By implementing similar strategies and approaches, you can make informed decisions, bridge the gap between market prices and fair values, and achieve greater success in your own investment endeavors.
Conclusion
Closing the Fair Value Gap for Informed Decision Making
Understanding and closing the fair value gap is vital for investors and businesses aiming to make informed decisions and achieve accurate pricing. Throughout this blog post, we have explored the concept of fair value gaps, identified the key factors contributing to them, and discussed strategies for bridging these gaps effectively.
By leveraging robust valuation methodologies, data-driven decision making, risk assessment, and transparency, you can minimize pricing discrepancies and achieve fairer assessments of an asset’s value. These strategies enable you to make informed investment decisions, enhance market efficiency, and build investor trust.
Remember, accurate pricing is the foundation for successful investing. By aligning market prices with fair values, you can capitalize on undervalued assets, mitigate risks, and maximize returns on your investments.
Closing the fair value gap requires continuous learning, adaptation, and a commitment to incorporating best practices into your decision-making processes. Stay updated on market trends, leverage reliable data sources, and embrace transparency in your interactions with stakeholders.
In conclusion, armed with the knowledge and strategies shared in this blog post, you are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of fair value gaps and achieve more accurate pricing. By bridging the gap between market prices and intrinsic values, you can unlock opportunities, make informed investment choices, and thrive in today’s dynamic financial landscape.
Happy investing, and may your journey be filled with success in closing the fair value gap!